In the daily life, we can see the centrifugal pumps everywhere. It is one of the necessary devices in the process system. The advantages of centrifugal pump are small volume, convenient operation and long service life. If the pipeline delivery system is compared to the blood vessel circulation system of the human body, the centrifugal pump is similar to the heart that delivers blood.
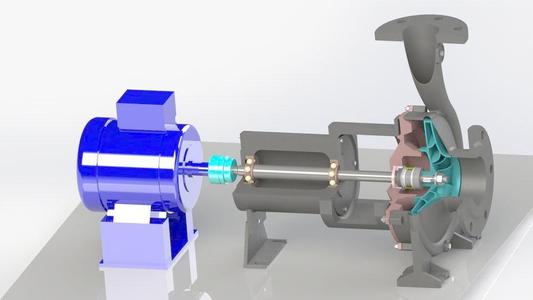
Centrifugal pumps consist of pump casing, impeller, pump cover and mechanical seal. It consists of pump shaft, bearing, bearing box, motor, base and other parts.

The key components of it are high-speed rotating impeller and fixed snail-shaped pump casing. As the main body of the water pump, the pump casing can play a role of fixed support. It connects with the bearing box bracket for mounting the bearing. Centrifugal pumps have impellers with several backward curved blades fastened to the pump shaft. The number of leaves is 4-12. The centrifugal pump rotates at high speed under the drive of the motor. Impeller plays the role of energy supply in centrifugal pump. The impeller can do work on the liquid in the pump. The suction pipeline connects with the suction port in the center of the pump casing. People install the one-way valve at the bottom of the suction line. The discharge line equipped with the regulating valve connects with the discharge port on the side of the pump casing.
After the centrifugal pump works, the impeller will rotate at high speed. This is under the action of the pump shaft. We can rotate the liquid pre-filled in the middle of the blade at a high speed. Under the action of inertial centrifugal force, the liquid will move to the outer periphery in the center of the impeller. When the liquid medium moves through the impeller, the liquid can obtain energy. This leads to an increase in static pressure energy. At the same time, the flow rate increases. When the liquid leaves the impeller and enters the pump casing, the flow rate of the liquid decelerates. This is under the condition that the flow passage in the casing is expanded. Finally, the liquid will flow tangentially into the pipeline. It is discharged. When liquid splashes from the center of the impeller to the outer periphery at high speed, low pressure area will be generated. This is in the center area of the impeller. Under the pressure difference, liquid can be sucked into the center of the impeller. Under the operation of the impeller, the liquid is sucked and discharged.
When starting the centrifugal pump, if there is no liquid in the pump body and suction pipe, the centrifugal pump cannot suck liquid. Because its suction port and discharge port connect with each other. The density of air is much lower than that of liquid. When there is no liquid in the impeller but only air, no matter how high-speed the impeller rotates, the inlet of the impeller cannot reach the vacuum required for liquid absorption. The centrifugal force generated will be small. The low pressure formed in the central area of the impeller is not sufficient to suck the liquid in the suction tank (storage tank) into the pump. In this way, the liquid cannot be absorbed. Filling the pump body and suction pipe with liquid or pumping out air is a must before the centrifugal pump is started.
The above is the basic introduction of centrifugal pump.